The articles and gender of nouns in Spanish
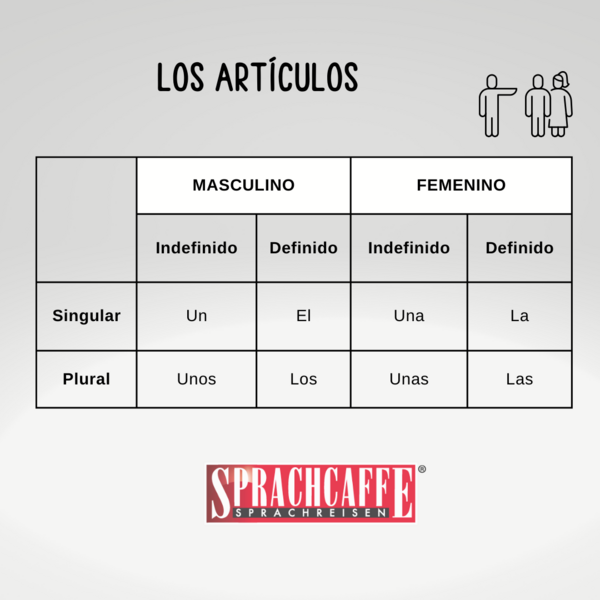
Articles, both definite and indefinite, play a crucial role in the Spanish language by providing essential information about the nouns they accompany. There are two types of articles: definite articles and indefinite articles. In Spanish, nouns have grammatical gender, that is, they are classified as masculine or feminine, although it is essential to keep in mind that the gender of the noun is not always related to the biological sex of the object or being to which it refers.
Spanish definite and indefinite articles
Spanish articles are classified into two types:
1. Definite articles: They determine a noun precisely, indicating that we are talking about something specific or known to the speaker and the listener. The choice of the definite article depends on the gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural) of the noun it accompanies. The definite articles in Spanish are "el", "la", "los" and "las".
| "El" and "los" |
|
| "La" and"las" |
|
2. Indefinite articles: They are used to refer to something in a non-specific or unknown way, that is, to express that we are not talking about a particular object or set of objects. The indefinite articles in Spanish are "un", "una", "unos" and "unas".
| "Un" and "unos": |
|
| "Una" and"unas" |
|
Spanish language trip
Improve your Spanish and have a wonderful holiday!
The gender of nouns in Spanish
Unlike other languages such as German, there is no neuter gender in Spanish. Nouns are classified into two genders: masculine and feminine.
- Masculine nouns: They are used to refer to beings, objects or concepts of masculine gender. Examples: the book, the dog, the tree, the day.
- Feminine nouns: They are used to refer to you are, objects or concepts of feminine gender. Examples: the house, the table, the chair, the night.
Rules for determining the gender of nouns
Often, nouns ending in -o are masculine, while those ending in -a are feminine.
- Examples: the cat (masculine), the window (feminine).
However, this rule is not absolute and there are many exceptions. Some of the most common nouns that break this rule are:
Masculine nouns ending in "a".
- El día (the day)
- El mapa (the map)
- El problema (the problem)
- El poema (the poem)
Feminine nouns ending in "o":
- La mano (the hand)
- La radio (the radio)
- La foto (the photo)
- La moto (the motorcycle)
Conclusion
|
With these tips you will learn more easily how to express the gender of nouns and articles. Don't forget to agree the article with the noun it accompanies! Memorize the rules and write down in a list the words that do not follow this rule. Put your knowledge into practice and travel to Spain or Cuba with Sprachcaffe to improve your Spanish.
Discover all options to learn Spanish abroad